Early diagnosis of Diabetes Mellitus and its treatment is very important. Typically the course of diabetes is chronic but without early treatment, chances of developing complications early is significant. Diabetes treatment is a lifetime affair but if managed and followed well, there is little or no deterioration in the quality of life for a long period.
Principles of treatment of Diabetes Mellitus :-
1) Control of hyperglycemia and related symptoms.
2) Reduce or eliminate the complications
3) Allow the patient to achieve a normal lifestyle.
Following methods are used in treatment :-
a) Diabetes education :- Person with diabetes should be educated about various signs and symptoms, self glucose monitoring, insulin self-injection, skin and foot care and hypoglycemic episodes.
b) Exercise :- Exercise forms an important part of prevention and treatment not only in Diabetes but also in other lifestyle related diseases like obesity, hypertension, stroke and other heart diseases. ADA recommends a min of 150min/week of exercise distributed over a period of at least 3 days. But it is important to monitor glucose before, during and after exercise. In case glucose level is high exercise should be delayed and if its low sugar based drink should be taken. Insulin doses should be reduced and its injections should be avoided in the exercising part.
c) Diabetes diet :- Optimal caloric intake coordinated with other aspects of Diabetes therapy is known as medical nutrition therapy. Following a proper diet plan is vital.
d)Medications :- Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus patients are exclusively dependent on insulin. Appropriate insulin regimens including combinations of long and short acting insulin are devised considering the patient's glycemic control and the dietary pattern. Type 2 diabetes patients require insulin only during acute episodes or mostly after a long period 10-15 yrs. So glucose lowering agents form the mainstay of the therapy. These drugs act either by reducing glucose production or by increasing its absorption via increase in insulin secretion or other mechanisms. One important thing about these drugs and insulin is that there is always a risk of having hypoglycemia. Especially when drug intake pattern or dietary pattern gets changed hence random changes in drugs or diet should be avoided as far as possible. We will discuss about the specifics of medications in subsequent posts.
e) Psychosocial aspect :- Given the profound impact of diabetes on life, it is very important. Persons having diabetes should understand that they are important members of the team. Achieving normoglycemia can be difficult or there may be deterioration in medical condition without any cause. Emotional stress can worsen the symptoms. Also eating disorders are relatively common in individuals with Diabetes.
We will discuss about the complications, their treatment and follow up/ongoing medical care in patients of Diabetes subsequently.
Meanwhile send us your views and queries, help others by sharing and tweeting this important information.
Principles of treatment of Diabetes Mellitus :-
1) Control of hyperglycemia and related symptoms.
2) Reduce or eliminate the complications
3) Allow the patient to achieve a normal lifestyle.
Following methods are used in treatment :-
a) Diabetes education :- Person with diabetes should be educated about various signs and symptoms, self glucose monitoring, insulin self-injection, skin and foot care and hypoglycemic episodes.
b) Exercise :- Exercise forms an important part of prevention and treatment not only in Diabetes but also in other lifestyle related diseases like obesity, hypertension, stroke and other heart diseases. ADA recommends a min of 150min/week of exercise distributed over a period of at least 3 days. But it is important to monitor glucose before, during and after exercise. In case glucose level is high exercise should be delayed and if its low sugar based drink should be taken. Insulin doses should be reduced and its injections should be avoided in the exercising part.
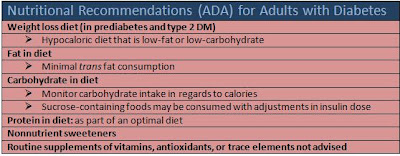
c) Diabetes diet :- Optimal caloric intake coordinated with other aspects of Diabetes therapy is known as medical nutrition therapy. Following a proper diet plan is vital.
 |
| (click to enlarge) |
d)Medications :- Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus patients are exclusively dependent on insulin. Appropriate insulin regimens including combinations of long and short acting insulin are devised considering the patient's glycemic control and the dietary pattern. Type 2 diabetes patients require insulin only during acute episodes or mostly after a long period 10-15 yrs. So glucose lowering agents form the mainstay of the therapy. These drugs act either by reducing glucose production or by increasing its absorption via increase in insulin secretion or other mechanisms. One important thing about these drugs and insulin is that there is always a risk of having hypoglycemia. Especially when drug intake pattern or dietary pattern gets changed hence random changes in drugs or diet should be avoided as far as possible. We will discuss about the specifics of medications in subsequent posts.
e) Psychosocial aspect :- Given the profound impact of diabetes on life, it is very important. Persons having diabetes should understand that they are important members of the team. Achieving normoglycemia can be difficult or there may be deterioration in medical condition without any cause. Emotional stress can worsen the symptoms. Also eating disorders are relatively common in individuals with Diabetes.
We will discuss about the complications, their treatment and follow up/ongoing medical care in patients of Diabetes subsequently.
Meanwhile send us your views and queries, help others by sharing and tweeting this important information.
Comments
Post a Comment
All Comments are subject to moderation.