Diabetes Mellitus is of 2 types - Type 1 Diabetes and Type 2 Diabetes. Whenever people talk about Diabetes in common parlance, almost every time they intend to speak about type 2 Diabetes because Type 2 Diabetes is much more common and known to people, than is type 1. Both have very different causes and treatment plans, prevention aspects also vary significantly. So its essential to understand the difference between the two.
Type 1 Diabetes and its monikers -
Type 1 Diabetes and its monikers -
- Early onset Diabetes Mellitus / Juvenile onset Diabetes Mellitus
- Insulin dependent Diabetes Mellitus (IDDM)
- Auto immune Diabetes mellitus
How do you get Diabetes type 1 ?
Most people believe Diabetes can only be due to lack of exercise, unhealthy eating or by putting on weight. No! None of it causes Type 1 Diabetes. Its actually caused by a combination of genetics and unknown environmental factors. Their is a genetic derangement, which when triggered by some unknown environmental factors or agents, cause autoimmune destruction of insulin producing Beta cells of pancreas. As a result insulin production goes on decreasing & Diabetes symptoms appear when more than 70-80% of cells are destroyed. This also explains the variable age of onset, as the time taken to reach that level of destruction varies from person to person. But it happens much earlier than type 2 Diabetes, hence most people get type 1 Diabetes in childhood or early adulthood. Hence the term Early onset Diabetes Mellitus.
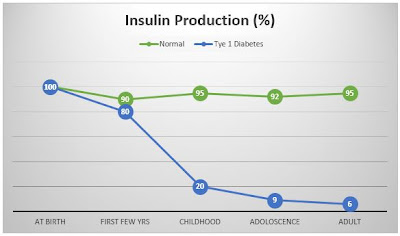 |
| Type 1 Diabetes (figures vary on individual basis) |
What symptoms and signs does it show?
Here are the detailed signs and symptoms of diabetes. In type 1 DM, classical triad of polydipsia (increased thirst), polyphagia (incresed hunger) & polyuria (frequent urination) is usually present. Additionally,in Type 1 DM, due to severe lack of insulin, sugar levels can rise to very high levels, which may cause a serious condition called Diabetic Ketoacidosis ( DKA) resulting in severe dehydration and even coma. Hypoglycemic symptoms like mental confusion, extreme fatigue, loss of consciousness may also occur on insulin overuse and inappropriate dietary habits. Also, Insulin is a major hormone participating in the growth and development of the body. Hence if their is very early onset (in early childhood), growth retardation may also occur. Type 1 DM is diagnosed on basis of sugar levels in blood (oral glucose tolerance test) and urine. Also, ketone levels are important if DKA is suspected.
What is treatment of type 1 DM ?
Simple! There is lack of insulin in body, hence what we should do is supplement it from our side. Blood Glucose levels must be checked regularly to adjust and stabilise Insulin requirement and avoid hyper or hypoglcemia. In addition, regular eye check-ups are advised due to fear of Diabetic retinopathy.
Prevention is unfortunately not an option currently but researchers are actively trying to find a vaccine against type 1 DM.
What complications can occur due to type 1 DM?
Diabetic Ketoacidosis is the most serious and feared complication. Others major ones are Retinal damage (Diabetic Retinopathy) , Damage to Peripheral Nerves and Blood vessels (Peripheral Neuropathy), Heart Disease and Stroke. Apart from these major ones, other minors include skin rashes, poor wound healing, gastric symptoms etc. We will cover them in detail in future posts.
We will be glad to answer any queries that you may have. Remember to share this info with your online friends and family.

Comments
Post a Comment
All Comments are subject to moderation.